
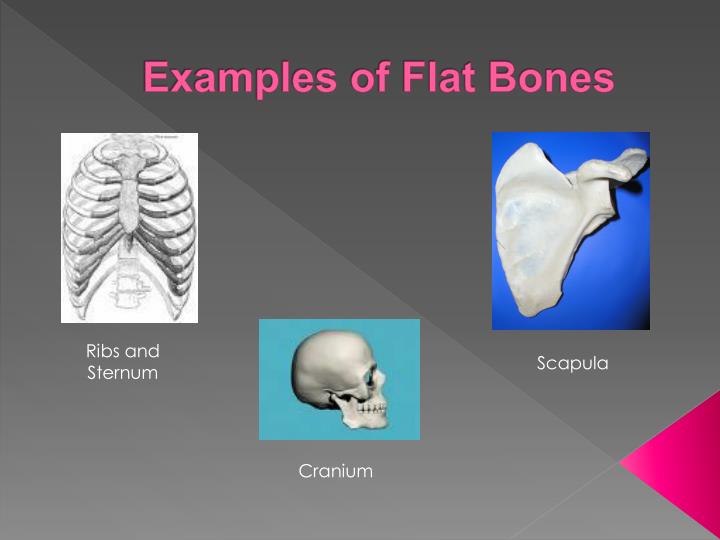
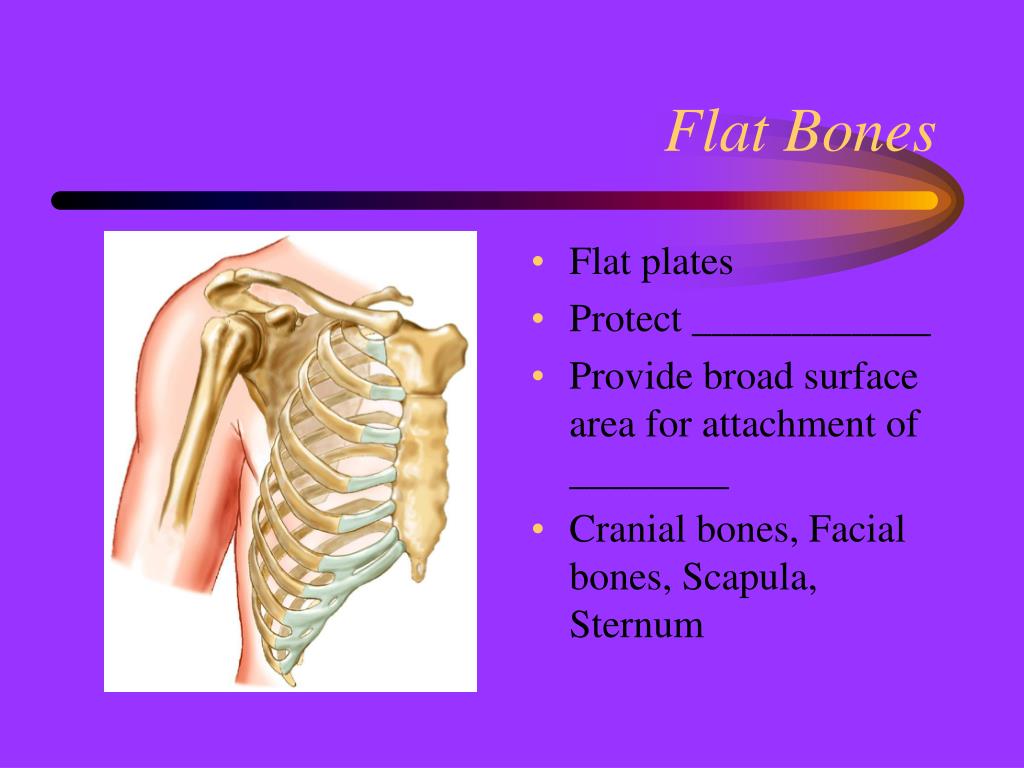
This definition was refined by the WHO to include measurement of bone. The intervening cancellous tissue is called the diploë, and this, in certain regions of the skull, becomes absorbed so as to leave spaces filled with air between the two tables. in vertebrae, and in flat bones such as the pelvis, whilst cortical bone is. In an adult, most red blood cells are formed in flat bones. Bone markings and the features of bones (including the correct words used to describe them) are often required by first-level courses in human anatomy and associated health science subjects. These bones are composed of two thin layers of compact bone enclosing between them a variable quantity of cancellous bone, which is the location of red bone marrow. In the cranial bones, the layers of compact tissue are familiarly known as the tables of the skull the outer one is thick and tough the inner is thin, dense, and brittle, and hence is termed the vitreous table. The irregular bones are bones which, from their peculiar form, cannot be grouped as long bone, short bone, flat bone or sesamoid bone. The flat bones are: the occipital, parietal, frontal, nasal, lacrimal, vomer, scapula, os coxæ, sternum, and ribs. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates, as in the cranium, the ilium, sternum, rib cage, the sacrum and the scapula.

Freebase Rate this definition: 4.0 / 1 voteįlat bones are bones whose principal requirement is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
